The gears of industry would not turn if not for power. In the modern world, we have come to depend on electricity generated from traditional fossil fuel resources like coal. However, amid a global awareness of the dangers of fossil fuels to our environment, we have since embarked on a paradigm shift towards renewable energy.
ASEAN Energy Outlook (2015-2040)
A step in the right direction was made in 2017 with the release of the fifth ASEAN Energy Outlook (AEO5) in Manila. The report was based on the energy policies of each ASEAN member state and its final results are based on each state’s expectations of their future energy landscape.
“The Outlook provides us with a pathway to address our long-term goals of achieving energy security, accessibility and affordability within the framework of sustainable development, as guided by our policy document, the ASEAN Plan of Action for Energy Cooperation (APAEC) 2016-2025,” said Philippine Secretary of Energy, Alfonso G. Cusi.
To conceptualise how the different possibilities of ASEAN’s regional energy landscape could pan out, the report outlines three separate scenario philosophies. The first is business as usual (BAU) – the maintaining of the status quo and assuming that member states develop no specific policies to reach their renewable energy and energy efficiency targets. The second is ASEAN member states target scenario (ATS) which assumes that the most recent renewable energy and energy efficiency targets of member states are reached. The third is the ASEAN progressive scenario (APS) which assumes regional targets as per the APAEC 2016-2025 are reached.
Power from renewables
As more and more people connect to their national grids, the demand for electricity will undoubtedly increase. Herein, lies a challenge for ASEAN member states to increase their respective electrification ratios (the number of people connected to the national grid) but to do so in a sustainable manner.
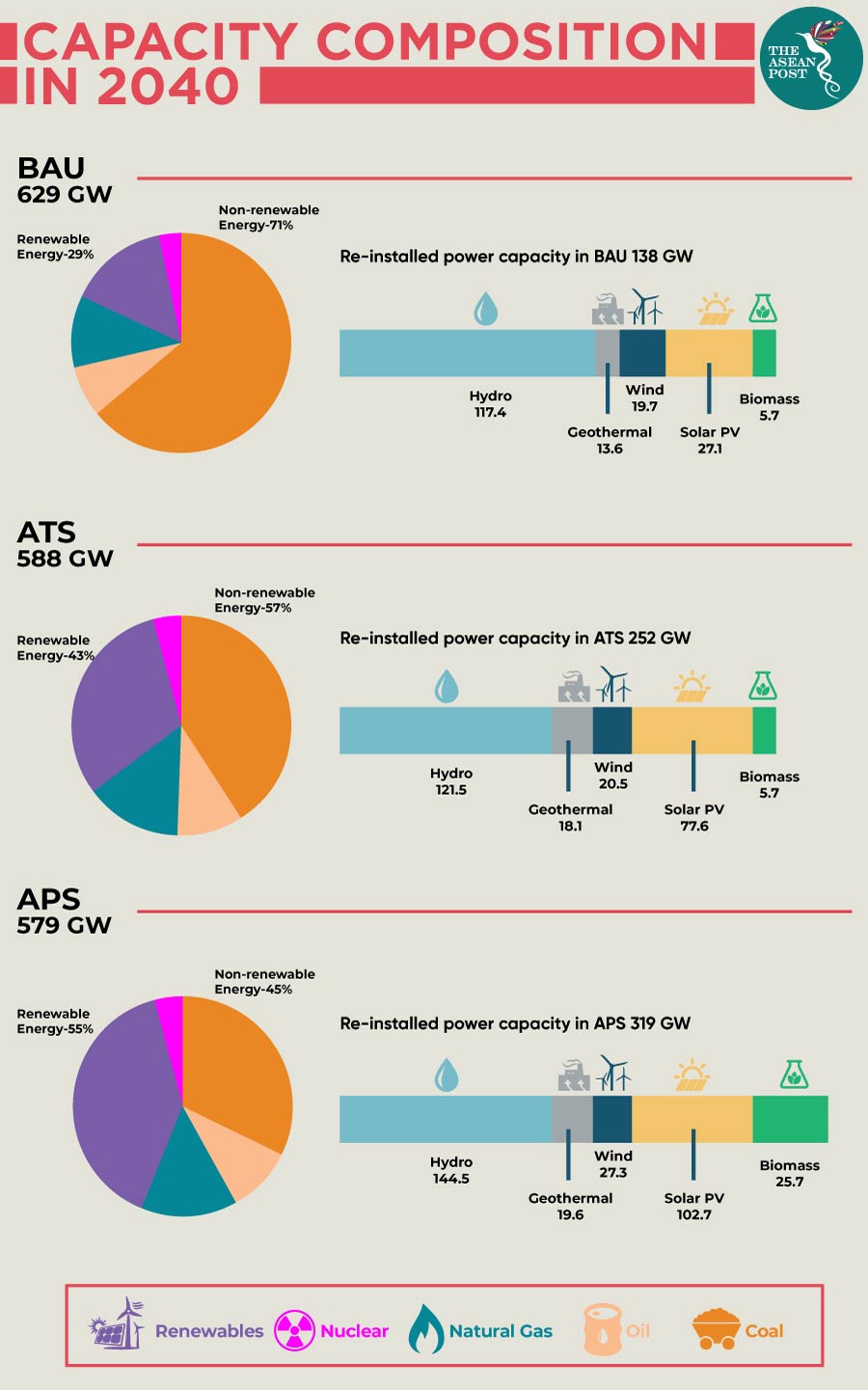
Under BAU projections, power capacity will increase 2.9 times to 629 gigawatts (GW) – of which 42.4 percent would be generated from coal with renewable energy generating only 29.2 percent.
However, under the ATS and APS scenarios, enhanced efficiency can significantly reduce installed capacity requirements. Under ATS, capacity requirements are 588 GW; 41 GW lower than BAU. Under APS, capacity requirements are 50 GW lower than BAU at 579 GW.
In all the scenarios, dependence on oil and gas continues to reduce while dependence on coal and renewable energy increases. Reliance on coal is due to the abundance of the fossil fuel and the surge in renewable energy power production is thanks to the cost effectiveness of the new technologies.
The report states that only through the APS scenario can ASEAN member states achieve the APAEC 2016-2025 target of a 23 percent renewable energy mix. Given that the highest contribution to renewable energy targets under APS comes from the power generation sector at 14.9 percent, member states must begin to fashion their national policies in line with this goal.
Interestingly, solar photovoltaics (PV) plays a significant role in APS compared to the other two scenarios. This is a result of increasingly cheaper costs of solar generation which could one day see solar as the prime source of renewable power generation in the region.
As the region moves towards a collective energy target with reduced dependence on fossil fuels and more emphasis on renewables, we cannot hope to achieve the end goal by bypassing the arduous steps that need to be taken along the way. The underlying reality is that power supply and generation have always been a national responsibility.
In order to build a strong foundation for regional-level cooperation or policy for power generation, ASEAN member states must develop their own national ambitions for renewable power. Only then can the policies be harmonised at a regional level towards the advancement of an ASEAN regional energy agenda.




