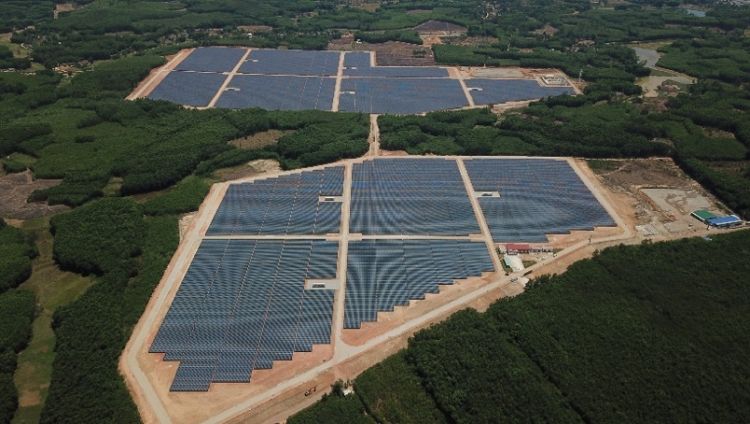
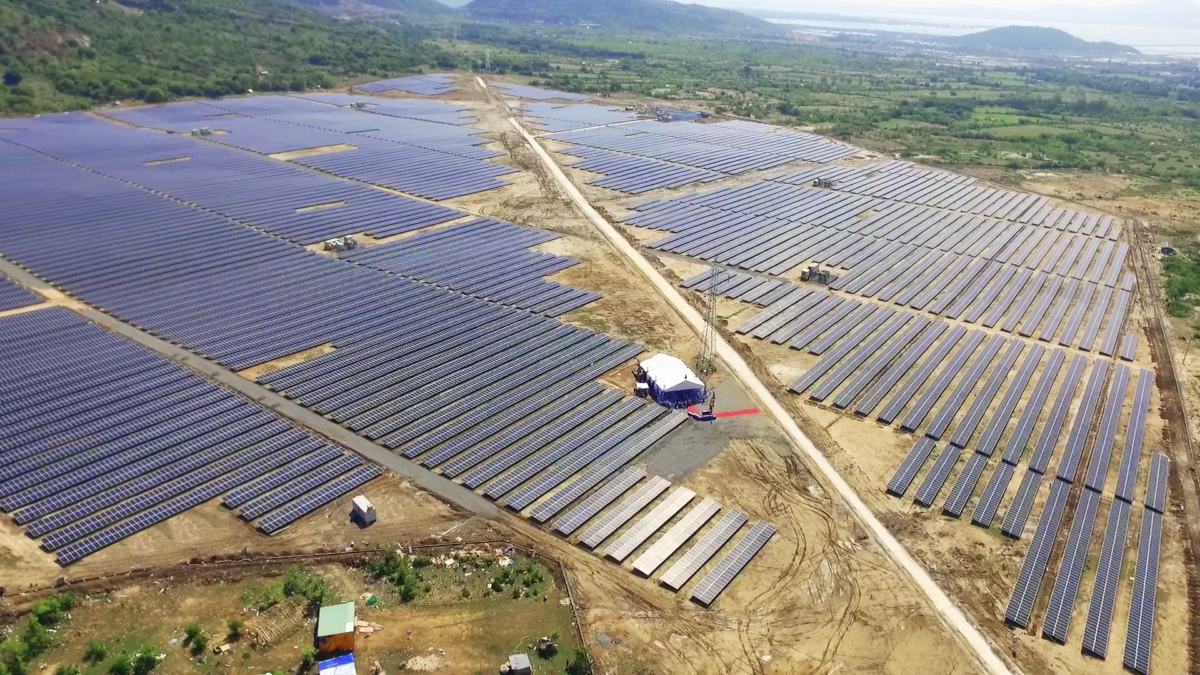
India’s Waaree Energies has commissioned a 49.5 MW ground-mounted solar project in Vietnam.
The project has been developed for Song Giang Solar Power on a 60-hectare site in Cam Ranh, Khanh Hoa province. It was completed in 120 days and is expected to generate more than 78,600 MWh of electricity per year.
The power generated by the plant will be sold to state-owned utility Vietnam Electricity, under a 20-year feed-in tariff (FIT) set by the Vietnamese government. Waaree Energies will handle O&M services for the $40 million installation.
“Everything including modules and even the structures were supplied from India,” said Sunil Rathi, director of Waaree Energies. “We were able to complete the project much before time, despite challenges like communication barriers and the loss of 30 working days to rain. Further, electricity transmission laws for the project requirements were completely different. Studying and meeting those requirements and consistently commissioning the project was a challenge.”
Vietnam is one of the 20 fastest-growing economies in the world, with average annual investments of $6.8 billion in the power sector. The government is targeting 12 GW of solar installations, with Rathi noting that energy demand is expected to rise by 10% by the end of this decade. “Waaree is targeting this growing demand,” he said.
Waaree Energies expects its international projects to account for over 15% of its overall revenue in FY2019-20. Its latest project in Vietnam marks the company’s completion of more than 600 MW of solar EPC projects.
“There is a big market globally, not just for PV panel supply, but also for EPC work, especially in countries like Vietnam, Cambodia and Thailand,” Rathi said. “We are in the process of signing more projects. We are also looking at African countries, where demand is very big.”
Overall, the company has an international pipeline of 100 MW. It has a presence in more than 280 locations across India and in 68 countries throughout the world. At 1.5 GW, it claims to have India’s largest solar PV module manufacturing capacity. It plans to expand its plant in the state of Gujarat to 2 GW by the next quarter.