Energy demand in building industry across ASEAN is projected to grow 2.6 times by 2050
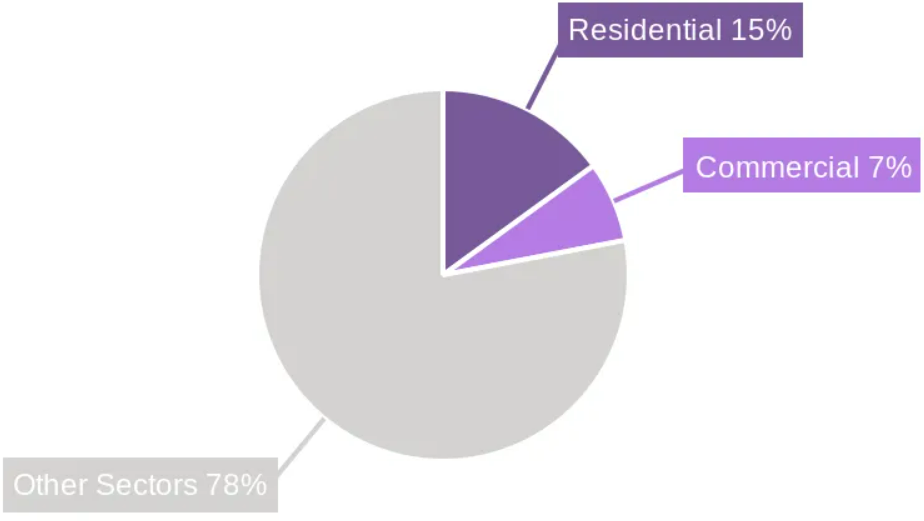
As one of the most energy-intensive sectors, the construction and building industries play a critical role in energy consumption and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Embodied carbon accounts for 10% of global energy-related GHG emissions and contribute up to 20-25% of a building's total life-cycle emissions. These are the result only from material production, transportation, and construction. At the same time, operational emissions from buildings had been calculated to be accounted for 21% of global GHG emissions and 22% of energy consumption in 2022. In ASEAN's tropical climate, rising temperatures have intensified cooling demand, further escalating energy use and emissions.
Building's share of energy consumption in 2022
Building Operation's share of CO2 Emissions in 2022
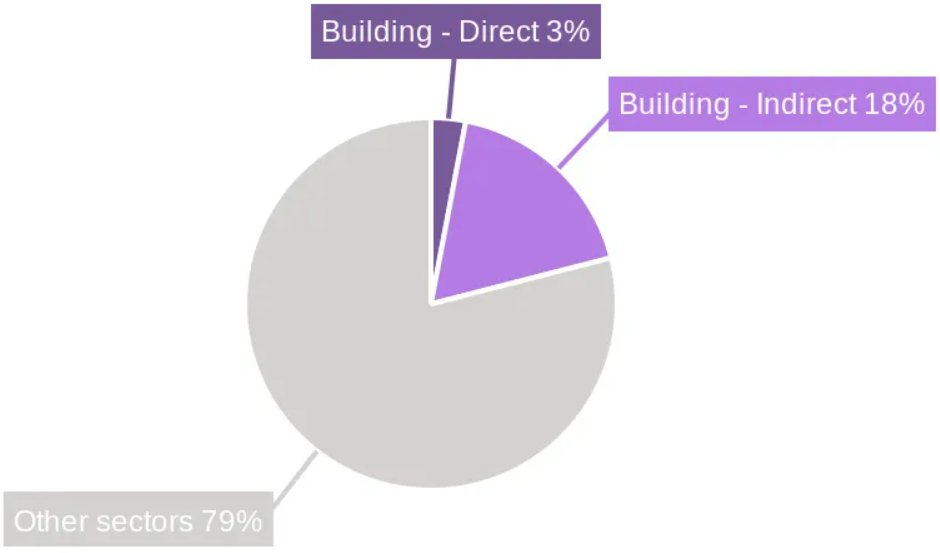
Source: 8th ASEAN Energy Outlook, 2024
Recognising the built environment's impact on regional and global decarbonization efforts, ASEAN Member States (AMS) have pledged their commitment to energy transition and net-zero carbon goals, aligning with the ASEAN Plan of Action for Energy Cooperation (APAEC) and Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Programme Overview
The Asia Low Carbon Buildings Transition (ALCBT) Programme is designed to integrate low-carbon building (LCB) practices into existing energy conservation policies in a wider range of Asia. Five countries have been selected as pilot sites, each requiring a unique approach tailored to its specific challenges. To accelerate the transition, ALCBT adopts a targeted and collaborative strategy, focusing on:

Cambodia
Cambodia
Building capacity and integrating energy regulations with monitoring tools.

India
India
Strengthening the implementation of building energy codes and promoting sustainable cooling.

Indonesia
Indonesia
Enhancing capacity, aligning green building regulations with government policies, and fostering an ESCO market.

Thailand
Thailand
Overcoming technical barriers and expanding energy efficiency services.

Vietnam
Vietnam
Advancing capacity for tracking building carbon stocks and addressing ESCO industry challenges, particularly in efficient cooling.
Through engagement with key stakeholders from governments, professionals, financial institutions, to academia, ALCBT aims to accelerate the adoption of low-carbon building practices and establish a strong foundation for sustainable energy transition.
The ALCBT Programme adds greater value to the growing Asian economies through top-down, bottom-up, and lateral approaches. By integrating policy development, public awareness, and industry engagement, ALCBT drives a smooth transition toward low-carbon buildings across Asia's built environment.
Goals & Targets
Direct and indirect emissions reduction
Reduction of 2.67 million tCO2eq GHG emission
Training of 19,000 Professionals
Mobilizing of €140 million in investments
Action Plans
Learn More About ALCBT
For inquiries please contact
[email protected]










