Menu
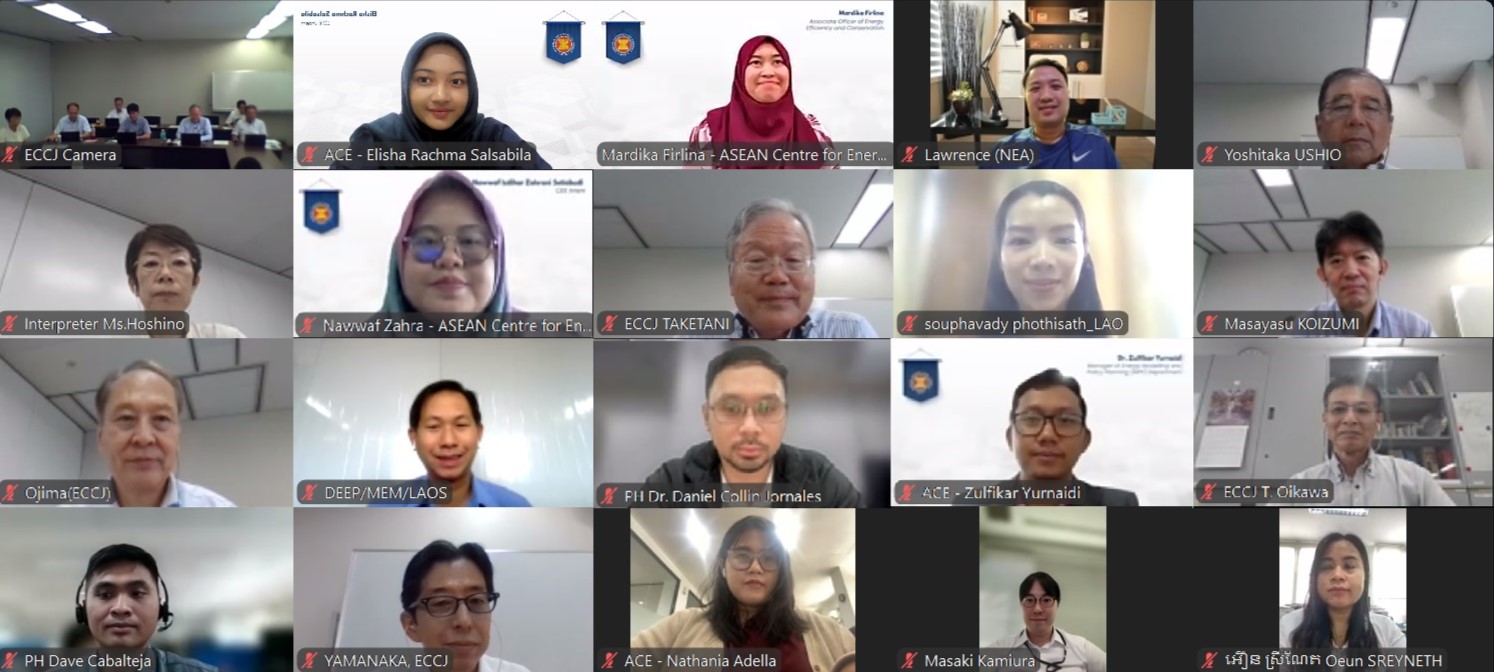
Photo 1. AJEEP CN Diagnosis Online Seminar Group Photo
The ASEAN Centre for Energy (ACE), in collaboration with the Energy Conservation Center Japan (ECCJ), successfully co-organised the ASEAN-Japan Energy Efficiency Partnership (AJEEP) Carbon Neutrality (CN) Diagnosis Online Seminar, held on 12 September 2024, as part of the ASEAN Senior Officials Meeting on Energy and Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (SOME-METI) Work Programme 2024-2025.
Participated by representatives from ASEAN Member States (AMS) — Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand, as well as representatives from ECCJ and ACE, the online seminar aimed to explain the CN diagnosis guidelines and implementation procedures for conducting the CN on-site diagnosis, including preparation of CN diagnosis reports and establishment of a medium to long term plan for CO2 reduction.
Photo 2. Opening Remarks by Masayasu Koizumi from ECCJ
The CN diagnosis, unlike conventional energy audits, emphasises knowledge sharing and capacity building for energy efficiency improvements in the ASEAN region by focusing primarily on the reduction of greenhouse gas and CO2 emissions. This programme aligned with the APAEC Phase II target to reduce energy intensity by 32% by 2025, supporting Programme Area No. 4 – Energy Efficiency and Conservation, particularly in industry and building sectors.
Under AJEEP Scheme 5, two CN diagnoses were successfully conducted in one industry in Malaysia and one building in Thailand in the previous fiscal year. In this fiscal year of 2024 – 2025, CN diagnoses will be expanded in two industries, one in Indonesia and one in Lao PDR, as well as in two buildings, one of which is in the Philippines.

Photo 3. Opening Remarks by Dr Zulfikar Yurnaidi, Head of ACE
The seminar commenced with opening remarks from Masayasu Koizumi, Managing Director of ECCJ, pointed out the importance of today’s seminar, which will focus on improved diagnostic methods for carbon neutrality, and urged participants to apply the insights gained to their own efforts. Followed by Dr Zulfikar Yurnaidi, Head of Energy Modeling and Policy Planning (MPP) and Energy Efficiency and Conservation (CEE) Department at ACE. He emphasised that AJEEP Scheme 5 plays a critical role in addressing climate change and increasing energy demand through capacity building and CN diagnosis, with a focus on reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Led by Mardika Firlina, Associate Officer of CEE Department at ACE, the seminar continued with four presentations regarding CN diagnosis. The first presentation, by Masaki Kamiura from the International Affairs Division, Agency for Natural Resources and Energy (ANRE), covered Japan’s energy efficiency policy. The presentation highlighted Japan’s efforts to reduce energy consumption while maintaining economic growth, the need to expand renewable energy to improve energy efficiency across various sectors, and the Top Runner Program, which sets energy efficiency standards for the target year based on the best-performing products in the market.

Photo 4. Mardika Firlina, Associate Officer of CEE at ACE
The second presentation by Noriaki Taketani, Deputy Director General of the Research and Solution Division, ECCJ, provided an explanation of CN project formation and CN diagnosis guidelines. The presentation outlined the steps involved in forming CN projects, including setting targets, and developing medium to long term plans. He also highlighted the importance of CO2 reduction measures and how CN diagnosis can help to identify areas for improvement in emissions reduction.
The next presentation by Hisafumi Ojima, Technical Expert, International Planning, Department International Cooperation Division, ECCJ, explained the practical CN diagnosis activity. The presentation covered the flow of CN diagnosis, including data collection, analysis, CN measures, and mid to long-term planning. He also highlighted key measures such as improving energy efficiency in processes, decarbonisation through fuel changes, and renewable energy.

Photo 5. Presentation by Hisafumi Ojima from ECCJ
The final presentation by Dr Yoshitaka Ushio, International Planning Department, International Cooperation Division, ECCJ, explained the Zero Energy Building (ZEB) design guidelines and diagnosis. The presentation covered the approach to achieving ZEB standards, including high-efficiency systems, as well as energy-saving technologies and renewable energy integration. Practical case studies of energy-efficient building designs were also discussed.

Photo 6. Presentation by Dr Yoshitaka Ushio from ECCJ
The seminar wrapped up with participants gaining valuable insights into carbon neutrality project formation, diagnosis, and energy-efficient building practices. The presentations provided practical guidelines that ASEAN Member States can apply in their efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance energy efficiency. With the support of AJEEP Scheme 5, these initiatives will play a key role in driving the region’s progress towards achieving carbon neutrality in the years to come.
ASEAN Japan Energy Efficiency Partnership (AJEEP) is a regional cooperation initiative between ASEAN and Japan. Since 2012, implemented by ACE and ECCJ, with financial support from METI, AJEEP is aiming to build the capacity and narrow the gap between AMS on EE&C policies and measures. Starting 2022, AJEEP entered into new Scheme 4 and Scheme 5. AJEEP Scheme 4 aims to support the establishment of the Sustainable ASEAN Energy Management Certification Scheme (SAEMAS). AJEEP Scheme 5 focuses on capacity building on advanced carbon neutrality technologies and systems to improve EE in industry, building, and transportation.
